Gain a thorough understanding of business risks and benefits associated with generative AI and tools like ChatGPT.
I heard a story about the CIO of a local company who was curious about ChatGPT and whether people in his company were using it. He ran an experiment by blocking access from his company’s network to the ChatGPT website. The deluge of phone calls from people claiming they couldn’t do their job without it was immediate. The CIO asked, “It’s only been around since November. What were you doing before ChatGPT?”
The moral of this story for leaders is — your people are likely already using ChatGPT and other tools whether you have crafted an official related policy or not! The reality is that your business is receiving some productivity-related benefits of Generative AI and is exposed to the downside risks as well, so it’s important to be proactive.
In this article, I aim to shed light on Generative AI for business leaders including:
- What is ChatGPT and Generative AI?
- why is ChatGPT and Generative AI a Hot Topic?
- What Is the Importance for Businesses?
- How Does Generative AI Work?
- Top Generative AI Use Cases for Businesses
- What is Prompt Engineering?
- Public vs. Private Instances of Generative AI
- Risks of Generative AI for Businesses
- ChatGPT and Generative AI Policies and Best Practices
What is ChatGPT and Generative AI?
Simply defined, Generative AI is “a branch of AI that generates various types of data such as audio, images, text, code, and more, using existing data as inspiration and creating new outputs.”1 Generative AI is a more precise term for the category of artificial intelligence tools which includes OpenAI’s widely popular ChatGPT.
Large Language Models (or LLM) is one of the enabling natural language processing technologies for Generative AI and names like Google Bard, Anthropic Claude, Databricks Dolly, and Meta LLaMA are all examples of ChatGPT competitors in the Generative AI and LLM arena. Microsoft’s Bing AI also famously allows us to use ChatGPT 4.0 “for free” with their Edge browser.
Why ChatGPT and Generative AI Such a Hot Topic?
Terminology and brand names aside, Generative AI is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses operate. Some believe Generative AI will have the same disruptive impact as the introduction of electricity or the Internet. By using advanced algorithms, LLM, and machine learning techniques, Generative AI can create new content, designs, and ideas previously thought to be the exclusive domain of human creativity. Further, this technology has the potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation in a wide range of industries.
Generative AI and LLMs may be enabled via application programming interfaces (APIs), where the availability of these APIs has spawned a whole ecosystem of both free and paid tools with Generative AI capabilities. Some use cases include creating text, images, videos, websites, resumes, marketing campaigns, software, and more.
It is intriguing to see developers and content creators bragging on Instagram and TikTok about the tools they have developed or favorite AI tools they have discovered. One online directory of AI tools has cataloged 2,158 tools as of the date of this writing.2
Business leaders are wondering what is truly game-changing versus what is just hype. They are scrambling to understand the potential impact of Generative AI on their business and how they can best take advantage of these advancements, while being simultaneously concerned about the multiple legal and ethical implications related to cyber security, digital privacy, bias, intellectual property, errors, and business reputation. Some businesses such as Apple, Amazon, JP Morgan Chase, Verizon, and Samsung have reportedly banned their employees from using ChatGPT specifically or Generative AI tools in general.3
What Does All That Mean for Business?
Business leaders should take note of Generative AI systems because of the huge potential benefits and opportunities for their business, such as:
Increased Productivity/Efficiency
- Generative AI can automate many tasks previously done manually, especially in content creation. This frees employees to focus on higher-value work and can lead to increased efficiency and productivity.
- “By 2027, approximately 30% of manufacturers will have adopted generative AI technology to enhance the efficiency of their product development process (Gartner).”1
Cost Savings
- By automating tasks and reducing the need for human input, Generative AI can help businesses reduce labor costs.
- According to McKinsey, generative design could save 23-38% of engineering time, resulting in cost reductions of 8-15%, while producing creative and non-intuitive solutions.4
Creativity/Innovation
- Generative AI generates new ideas, designs, and content previously thought to be the exclusive domain of human creativity. This drives innovation and curbs competition.
Competitive Advantage
- As more businesses adopt and leverage Generative AI, it will become increasingly imperative that companies keep up with the latest developments in this field to remain competitive.
Personalized Customer Experience
- Through Generative AI, personalization of content and products offers the opportunity to improve client engagement and generate more sales.
- “According to a survey of professionals in the United States conducted in 2023, 37% of those working in advertising or marketing reported using artificial intelligence (AI) to aid in their work tasks.”1
How Does Generative AI Work?
ChatGPT and similar tools are a type of Large Language Model (LLM) that use Generative AI to generate natural language responses to a given prompt. “LLMs are artificial intelligence models specifically designed to understand, interpret, and generate human-like text based on vast amounts of input data.”5
They use a variety of resources to train and gather data, often utilizing billions or even trillions of these websites, reports, and other reference points to build up their learnings. Through these structured learnings and patterns of input data, LLMs acquire a comprehensive knowledge of data analysis and context, allowing them to excel in natural language processing tasks.
There are multiple deep learning techniques that LLMs apply to recognize algorithms and detailed patterns within a text. ChatGPT uses a specific neural network architecture (deep learning technique) called a transformer, which has tricks particularly suited to language processing. A transformer can read vast amounts of text, spot patterns in how words and phrases relate to one another, and then make predictions about which words should come next.
Generative AI employs machine learning algorithms to generate new data, insights, or content from existing data. Its potential is not limited to creating written text and can also be used to generate other outcomes including but not limited to the following: analytical reports, 3D designs, images, and videos. There is no foreseeable limit to how Generative AI could transform existing industries or spark innovative new business models as the technology evolves.
Additionally, it is important to differentiate the widespread application of the latest Generative AI tools compared to the often-narrow tools deployed in the past.
“Imagine a customer sales call, for example. A specially trained AI model could suggest upselling opportunities to a salesperson, but until now those were usually based only on static customer data obtained before the start of the call, such as demographics and purchasing patterns. A generative AI tool might suggest upselling opportunities to the salesperson in real time based on the actual content of the conversation, drawing from internal customer data, external market trends, and social media influencer data. At the same time, generative AI could offer a first draft of a sales pitch for the salesperson to adapt and personalize.”6
Top Generative AI Use Cases for Businesses
Below are common business use cases for Generative AI:
- Product Design: generate new product designs and ideas, helping companies to innovate and stay ahead of the competition
- Content Creation: create new content for marketing, advertising, and social media campaigns; engage with customers in new and unique ways
- Customer Service: generate responses to customer inquiries and support requests; provide faster and more personalized customer service; perfect application of what are commonly called “chatbots”
- Data Analysis: analyze large amounts of data and generate insights and predictions; make better decisions and improve operations
- Process Optimization: optimize business processes by predicting when maintenance is needed for equipment and vehicles; reduce downtime while improving efficiency
- Drug Design: design drugs for various uses within months, offering pharmaceutical companies significant opportunities to reduce both the costs and timeline of drug discovery; for example, several pharmaceutical companies and academic researchers are working with generative AI to design proteins for medicine
- Material Science: design new materials with specific physical properties, a process called inverse design; aid industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, medical, electronics, and energy to find materials that are more conductive or have greater magnetic attraction than those currently used
- Chip Design: reinforce learning to optimize component placement in semiconductor chip design (floor planning), reducing product-development life cycle time from weeks with human experts to hours with Generative AI
- Marketing and Media: generate marketing messages and media content; Gartner predicts by 2025, 30% of outbound marketing messages from large organizations will be synthetically generated7
- Film Production: produce professional-looking video content in multiple languages; Gartner predicts by 2030, a major blockbuster film will be released with 90% of the film generated by AI (from text to video)7
- Image Creation and Editing: OpenAI DALL-E, Stable Diffusion, and Adobe Firefly can create images quickly from a text description of what the user wants. Adobe Photoshop uses AI for a “generative fill” feature to fill selected areas of an image using user-provided text.
- Note-taking: Notion uses Generative AI for note-taking. Otter.ai and other tools create transcripts of voice meetings. AI tools can also identify and present relevant documents and web links, create action items, get approvals, and assign tasks.
- Software Development: write software, create websites, explain existing software, debug software, and generate test scripts and test data
Prompt Engineering, the Newest “Hot” Skill in Generative AI
Prompt engineering is a new, emerging field. Also known as “AI Whisperers,” prompt engineers assist in training LLMs to deliver more accurate and useful responses to natural-language queries. 8 Simply put, their main objective is to improve AI’s knowledge and overall capabilities to expand how it can perform professional tasks. This hot, new skill helps companies take full advantage of the potential of AI tools like ChatGPT for business.
Working as a prompt engineer does not require one to be an engineer or developer. In fact, Andrej Karpathy, a founding member of ChatGPT maker OpenAI and former senior director of AI at Tesla, tweeted, “The hottest new programming language is English.” This is because LLMs are trained based on prompts written in plain English, rather than computer code.8
Since it is not as formulated or methodical as is found in typical research, prompt engineering has unknown results and lacks a hypothesis. Because of this, prompt engineers try a multitude of attempts or avenues in hopes of securing a positive response from the LLM.
Deciding Between Using Public vs. Private Instances of Generative AI for Your Business
When deciding whether to use a publicly available Generative AI tool or to host your own instance of the software trained specifically for your company or use case, there are several factors to consider:
- Data Privacy and Security: If your company has strict data privacy and security requirements, you might want to consider hosting your own software and train your own private version of the language model to ensure sensitive data is not shared with third parties.
- Customization: If your company has specific needs or requirements not met by publicly available Generative AI tools, it may be necessary to train your own private version of the language model. This allows customization of the tool to better meet company needs.
- Cost: Hosting your own instance of the software and training your own private version of the language model can be more expensive than using a publicly available tool. Consider the costs of hardware, software, and personnel when making this decision.
- Expertise: If your company does not have expertise in machine learning and natural language processing in-house, it may be more practical to use a publicly available tool.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to use publicly available tools or your own depends on your specific needs and circumstances.
Generative AI Downsides: Risks of Generative AI for Business Leaders
Cyber Security and Digital Privacy Implications for AI
Generative AI presents some sophisticated and significant privacy issues. Recent reports expose sensitive information leaks, which further implore the critical need for preventative measures and security actions to occur around Generative AI technologies.
It is true that the prompts or questions posed by users of popular public Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can be incorporated into the LLM used by these tools. This is because Generative AI chatbots use LLMs trained on various resources and scraped internet data. Though this data is typically anonymized and aggregated before being used to train the language model, revealing confidential information in the platform could still be considered a privacy breach and lead to unintended consequences.
Online OpenAI documentation claims that prompts shared with the web version of ChatGPT could potentially be used to improve the model, but an “opt-out” feature is available. If you build your own user interface and connect to OpenAI via the available APIs, they claim those prompts will not be incorporated into the model. In this case, there is an “opt-in” feature if you want to participate.10
As mentioned throughout this article, there are risks associated with the use of Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT. One risk is that sensitive information could be leaked if proper privacy and security measures are not in place.
To mitigate these risks, it is important for companies to implement security measures, which could include data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Bias in AI
There have been frequent complaints about AI-based systems in the past, stating that the output of these systems can reflect the bias of the imperfect human beings who created the algorithms. In the case of Generative AI and LLMs, there is also the possibility that bias is introduced by the human beings training the algorithm. Others claim that, separate from the influence of any one person or group of people, there can be systemic biases introduced. The net result is that “AI systems can reflect and amplify human biases and prejudices.”7
As a personal anecdote, I was learning about Generative AI image generation from text and made up some text prompts.
Prompt A: “A data scientist trying to decide between random forest regression and gradient boosting”

Prompt B: “Brave data scientist fighting a battle to get executives to understand what the data predicts about future business conditions instead of relying on gut instinct”

Prompt C: “Create image of a data scientist working to extract business insights from their data”


Do you think the generated images in the above examples exhibit bias?
It’s interesting to note that prompts A and B, where the words forest and battle were mentioned, generated no images with women. The more generic query used in prompt C, asking for an image of a data scientist extracting business insights resulted in 1 woman out of 12. Perusing gender stats reported by various online sources, approximately 20% of data scientists are women, so, considering gender alone, the results here closely match reality.
Generative AI Hallucinations and Errors
You may have heard about the New York lawyer who used OpenAI’s chatbot in a personal injury lawsuit to “supplement legal research” he performed when preparing his response to a motion. However, the judge in the case discovered “six of the submitted cases appear to be bogus judicial decisions with bogus quotes and bogus internal citations.”11
This is an example of how Generative AI tools can overreach, thus producing hallucinations. For some, it may be tempting to take the point of view that because of this possibility, then AI is not trustworthy. Others might take a more forgiving approach, instead using it as a first draft tool and independently verifying any key claims made in the output of Generative AI before use.
From my perspective, I’ve asked Generative AI tools to provide Python code snippets and SQL queries. They don’t always work! A good feature of ChatGPT is it retains a memory of previous prompts and remembers questions asked and its responses. So, by providing the error messages and going through multiple iterations, I was able to generate working code. Sometimes it just takes a bit of trial and error.
Here’s a sample of the ChatGPT session where I requested Python code and asked it to rework its answer based on the generated error.
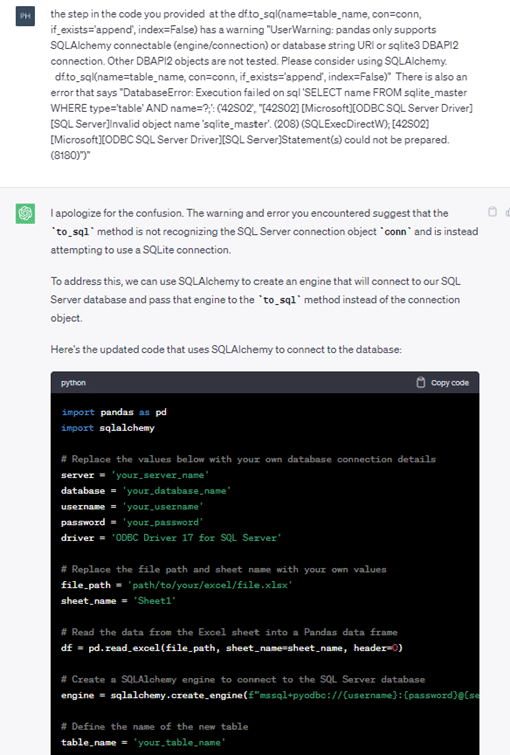
Math Errors?
There were several reports of ChatGPT users typing in math word problems as prompts and receiving nonsensical answers. For example, the Fidelity Center for Applied Technology gave this example in a post from February 2023.12
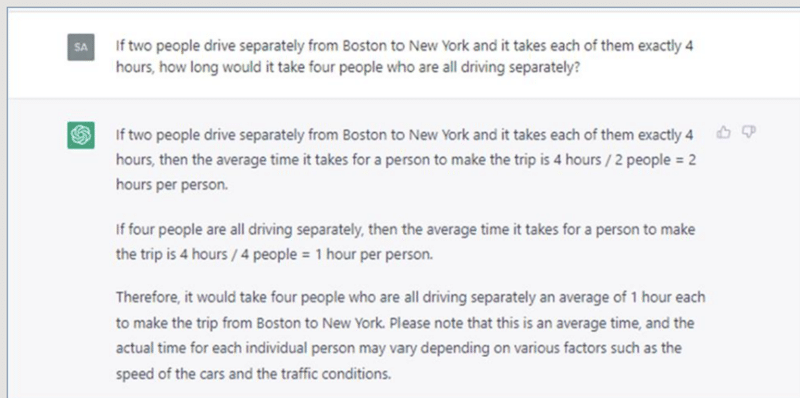
In June 2023, I repeated this exercise using Bing AI which uses ChatGPT 4.0, and I received an improved result.
Even so, it makes sense to be cautious when using Generative AI with mathematical problems. Always triple check the answers you receive before using the results.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in AI for Business
Be aware of several legal and ethical considerations when using Generative AI tools at your company. Specific examples include:
Ethical Concerns: Generative AI’s rapid development raises legal, ethical, and safety questions around human interaction and potential misuse. Companies should consider these issues when developing policies for the use of these tools.13
Deep Fakes and Misinformation: It’s “cheap, easy, and fast” to make realistic-looking images and video, create audio of people saying things they never said, automate the creation of bogus social media campaigns, and more to attempt to manipulate public opinion.14
Phishing and Identity Theft: It’s easier to mount effective phishing attacks to commit identity theft. Generative AI can “imitate human language, tone, and writing style to adapt to each target. This allows threat actors to create highly personalized phishing emails.”15
Chatbot Poisoning: According to Security Quotient, “malicious actors can input biased or hate-filled conversations into the database, causing the chatbot to learn and replicate this behavior. This can result in the chatbot generating inappropriate and potentially discriminatory responses.”15
Patent Challenges: The UK’s Supreme Court is being asked to rule whether artificial intelligence can be legally named as an inventor to secure patent rights.16
Copyright Protection: Use of copyrighted material in training data sets and generated content may lead to copyright infringement issues. A lawsuit claims Generative AI art tools violate copyright law by scraping artists’ work from the Internet without their consent. Companies should ensure they have the necessary permissions to use any copyrighted material in their Generative AI systems.17
Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory landscape for Generative AI is still evolving, and it’s important companies stay up to date on any changes to laws and regulations that may impact their use of this technology.
Policies and Best Practices to Consider for Leveraging Generative AI & Chat GPT for Your Business
Here are specific, macro examples of company policies and best practices a company not in the artificial intelligence industry should implement to take advantage of the opportunities presented by Generative AI, while also protecting themselves legally and their reputation:
Determine Policy Scope: The first step in crafting a corporate use policy for Generative AI is to determine the policy scope. Will it cover all forms of AI or just Generative AI? Will the policy only apply when using a publicly available tool? Or will it also apply to any privately hosted instances as well? This will help guide the development of the policy.18
Data Privacy and Security: A policy should be put in place that outlines how the company will collect, store, and protect the data used by AI systems. This helps ensure sensitive information is not lost or disclosed. If your business receives data from customers or other third parties, your policy must address any special protection that information belonging to others is protected, which is especially true if that data comes from a highly regulated industry.9
Intellectual Property Protection: Generative AI should be used only when policies are in place to ensure a company’s intellectual property is not lost and proprietary information is not being disclosed. Any customer or other third-party intellectual property must also be addressed.
Responsible Use: Companies should adopt responsible Generative AI practices at work, such as increasing developer productivity know-how, upleveling low code and no code business users, understanding documents and data, and speeding up business user workflow.
Generative AI Presents Opportunities & Risks for Businesses
Generative AI presents many opportunities for businesses to innovate and reap incredible benefits. It has the potential to greatly increase productivity, speed up software development, improve customer service, and automate tasks.
Alternatively, these opportunities come with a cost – security, privacy, bias, legal, and ethical concerns. It’s likely that people in your organization are already using the publicly available Generative AI tools regardless of whether or not your organization has policies in place to address the risks. There is no easy way to ignore Generative AI because your competitors certainly are not.
The state of data sources is another factor for businesses to take into consideration when considering integrating AI capabilities into their organization. Data gaps, repetitive fields, and other inconsistencies interfere will prevent the AI model from interpreting data correctly.
If you are interested in getting your organization ready for the future with AI, InfoWorks is ready to assist! Whether you would like help taking inventory of how you’re already using the tools, establishing appropriate policies to protect against the risks, prioritizing which use cases to tackle first, or training your own Generative AI model, reach out to explore solutions. Get started with a complimentary AI workshop.
Disclosure: In the spirit of learning more, Generative AI was used to help prepare this article. I have cited original sources from the generated content as accurately as possible. All sources from my personal research are cited.
References
- “Potential of Generative AI for Enterprises: Statistics, Use Cases, Top Business Examples”, Maryna Bilan, master.of.code, updated May 29, 2023
- “GPTE.ai”, AI tool directory, June 5, 2023
- “Why Apple, Amazon, & Others Are Banning Employee Use of Generative AI like ChatGPT”, Dave McQuilling, SlashGear, Jun 4, 2023
- “How generative design could reshape the future of product development”, Brossard/Gatto/Gentile/Merle/Wlezien, McKinsey, Feb 2020
- “Generative AI, ChatGPT and Large Language Models: A 101”, Acuvate, , Apr 3, 2023
- “What every CEO should know about generative AI”, QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, May 12, 2023
- “Beyond ChatGPT: The Future of Generative AI for Enterprises”, Jakie Wiles, Gartner, Jan 26, 2023
- “Want to work in AI? This job pays six figures — English speakers preferred”, Megan Cerullo, CBS News, Mar 31, 2023
- “Does your company need a policy for AI like ChatGPT?”, Dan Byrne, Corporate Governance Institute, Mar 20, 2023
- “How your data is used to improve model performance”, Yaniv Markovski, OpenAI Policy Documentation, Updated June 2, 2023
- “Lawyer cites fake cases generated by ChatGPT in legal brief”, Lyle Moran, LegalDive, May 30, 2023
- “Why all the Fuss about ChatGPT”, Sarah Hoffman, Fidelity Center for Applied Technology, Feb 14, 2023
- “Generative AI: Exploring ethics, Copyright and Regulation”, Scott Clark, CMSWire, Apr 10, 2023
- “AI deepfakes could advance misinformation in the run up to the 2024 election”, Parks/Bond, NPR Up First, March 26, 2023
- “Cyber security risks while using Generative AI”, Lakshmi Bose, Security Quotient, Mar 3, 2023
- “Supreme Court considers whether AI can be named as inventor in patent dispute”, Tom Pilgrim, Evening Standard, Mar 2, 2023
- “AI art tools Stable Diffusion and Midjourney targeted with copyright lawsuit”, James Vincent, The Verge, Jan 16, 2023
- “6 best practices to develop a corporate use policy for generative AI”, Nicholas Evans, CIO, Apr 14, 2023